Loss of consciousness due to exposure to H₂S
A member has reported an incident in which two crew members lost consciousness owing to exposure to Hâ‚‚S. The incident occurred when a team of three mechanics were assigned to clean the starboard-side sewage tank. The operations started at the beginning of the shift, the team opened the hatch on top of the sewage tank to clean the residual materials (settling tank was half full). One of the mechanics, standing on top of the roof of the tank, was spraying high pressure water in order to break the solidified layer of slurry. During this process Hâ‚‚S gas trapped under the solidified material escaped, reaching the mechanic who lost consciousness.
A second member of the team went on top of the tank in order to help the colleague, but he fell unconscious as well. The third member did not go on top of the tank instead, he raised the alarm. However, he remained inside the room and as the Hâ‚‚S descended from the tank (being heavier than air) it intoxicated the third team member who as a result began to feel dizzy.
The emergency team arrived at the scene and rescued the two unconscious mechanics and the third team member. All three persons made a full recovery after administration of oxygen by the doctor.
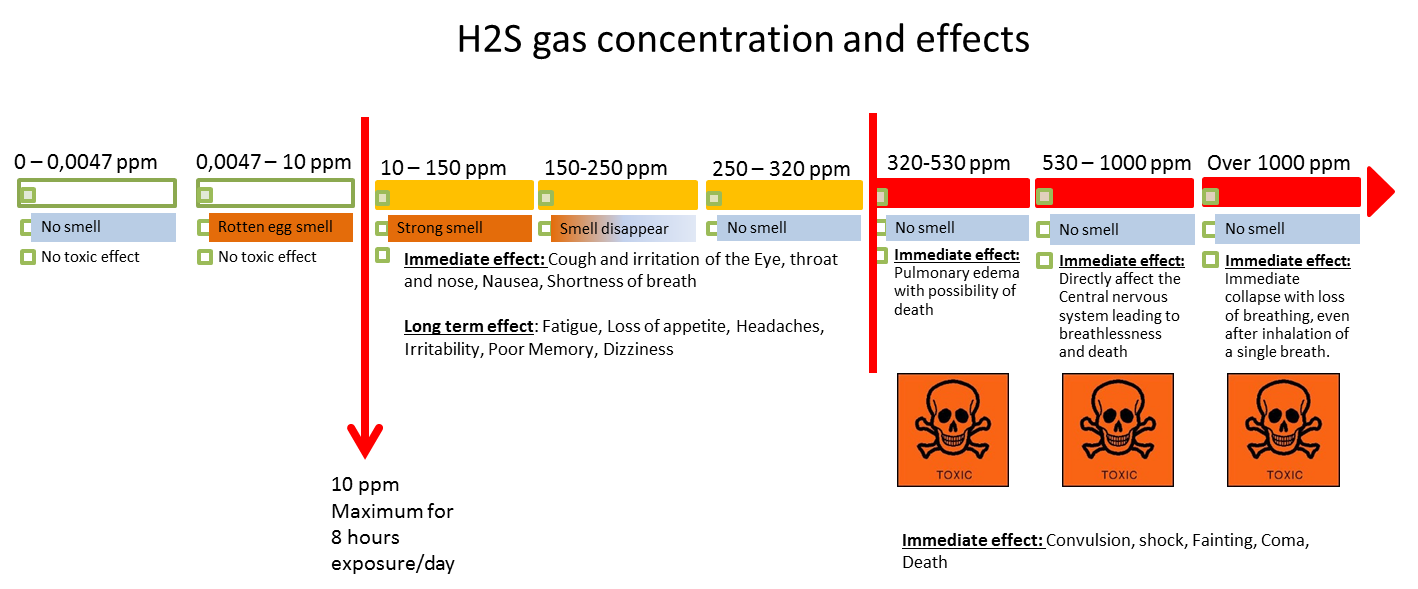
Our member’s investigation revealed the following causes:
- Lack of compliance with manufacturer instruction (e. g. de-sludge procedure, procedure for long period of shut down of sewage tank, etc.);
- Hazards related to potential presence of toxic gases (e.g. Hâ‚‚S) were not identified in the job safety analysis or the toolbox talk. As a consequence, a permit to work (PTW) process was not applied;
- Inadequate work planning and supervision: the injured persons were over confident that they could perform a cleaning task they had done before in the same way;
- The sewage plant room was not equipped with gas detection system.
Our member took the following corrective actions:
- Considered the installation of a gas detection system in the area;
- Reviewed the operation and maintenance manual of the sewage treatment tank and new procedures developed;
- Ensured proper planning, risk assessment and execution of these operations, including the use of PTW;
- Reviewed job safety analysis for cleaning of sewage tank;
- Organised refresher training for job safety analysis (JSA), hazard identification, PTW etc. for all personnel involved in tank cleaning;
- Organised confined space entry training for key personnel (authorized gas tester, confined space awareness and rescue);
- Reviewed manufacturer requirement about installation of a dedicated sewage holding tank onboard for the de-sludge operations.
The following lessons were learnt:
- Any maintenance on sewage treatment tanks requiring the opening of the tank itself should be considered as hazardous due to the potential release of toxic gases:
- In principle, such maintenance should be conducted using exactly the same precautions as for work in confined spaces;
- Manufacturer instructions (in this instance, for installation, operation and maintenance of the sewage tank) should be followed;
- Any deviation from the instructions, or any modification of the equipment itself, should be approved through the management of change process.
Safety Event
Published: 13 March 2014
Download: IMCA SF 03/14
IMCA Safety Flashes
Submit a Report
IMCA Safety Flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing lessons to be more easily learnt for the benefit of all. The effectiveness of the IMCA Safety Flash system depends on Members sharing information and so avoiding repeat incidents. Please consider adding [email protected] to your internal distribution list for safety alerts or manually submitting information on incidents you consider may be relevant. All information is anonymised or sanitised, as appropriate.
IMCA’s store terms and conditions (https://www.imca-int.com/legal-notices/terms/) apply to all downloads from IMCA’s website, including this document.
IMCA makes every effort to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data contained in the documents it publishes, but IMCA shall not be liable for any guidance and/or recommendation and/or statement herein contained. The information contained in this document does not fulfil or replace any individual’s or Member's legal, regulatory or other duties or obligations in respect of their operations. Individuals and Members remain solely responsible for the safe, lawful and proper conduct of their operations.
