Injury involving contact with a vehicle battery
- Safety Flash
- Published on 1 February 2003
- Generated on 12 July 2025
- IMCA SF 02/03
- 1 minute read
Jump to:
A 12 volt vehicle battery was being disconnected using a crescent wrench, which slipped and grounded out when it came in contact with metal.
What happened?
The person received a burn on his ring finger as his gold ring had come into contact with the wrench. The injury was completely around the ring finger and severe enough to cause concern about the loss of the finger from a lack of adequate circulation.
It has been pointed out that most vehicle batteries have 600-800 cranking amps, compared to 75 amps for stick welding and 300 amps for air arc welding. Severe burn injuries can occur and caution should be exercised when handling such batteries, including removing rings and other jewellery before starting work near or on a battery/connected wires and equipment.
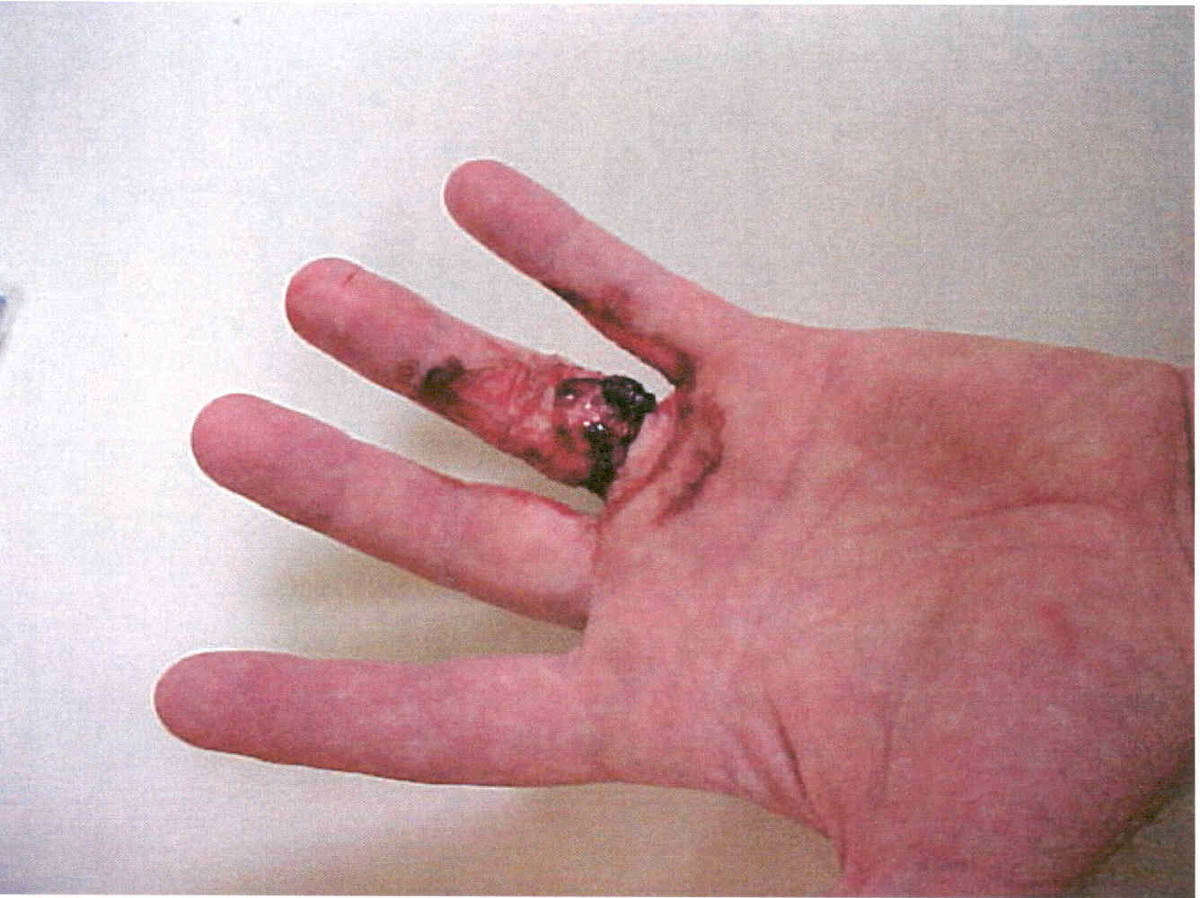
injured finger
IMCA Safety Flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing lessons to be more easily learnt for the benefit of the entire offshore industry.
The effectiveness of the IMCA Safety Flash system depends on the industry sharing information and so avoiding repeat incidents. Incidents are classified according to IOGP's Life Saving Rules.
All information is anonymised or sanitised, as appropriate, and warnings for graphic content included where possible.
IMCA makes every effort to ensure both the accuracy and reliability of the information shared, but is not be liable for any guidance and/or recommendation and/or statement herein contained.
The information contained in this document does not fulfil or replace any individual's or Member's legal, regulatory or other duties or obligations in respect of their operations. Individuals and Members remain solely responsible for the safe, lawful and proper conduct of their operations.
Share your safety incidents with IMCA online. Sign-up to receive Safety Flashes straight to your email.