The Zika virus
- Safety Flash
- Published on 3 March 2016
- Generated on 1 March 2026
- IMCA SF 06/16
- 3 minute read
Jump to:
Zika is a disease caused by the Zika virus – it is spread to people primarily through the bite of an infected Aedes species mosquito.
Symptoms
About 1 in 5 people infected with Zika will get sick. For people who get sick, the illness is usually mild. For this reason, many people might not realise that they have been infected. The most common symptoms of the Zika virus disease are fever, rash, joint pain, or conjunctivitis (red eyes). Symptoms typically begin 2 to 7 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. The illness is usually mild with symptoms lasting from several days to a week.
Transmission
The Zika virus is transmitted to people primarily through the bite of an infected Aedes species mosquito. These are the same mosquitoes that spread Dengue and Chikungunya viruses. These mosquitoes are aggressive daytime biters, but they can also bite at night. Mosquitoes become infected when they bite a person already infected with the virus. Infected mosquitoes can then spread the virus to other people through bites. Spreading of the virus through blood transfusion and sexual contact have also been reported.
At risk areas
Currently, South America is seeing a large outbreak of the Zika virus infection, with Brazil reporting the largest outbreak – estimated at over 1 million infections in 2015. Within South East Asia, sporadic cases of the Zika virus have been detected from Cambodia, Indonesia, Philippines, East Malaysia and Thailand in recent years.
The control measures are as follows
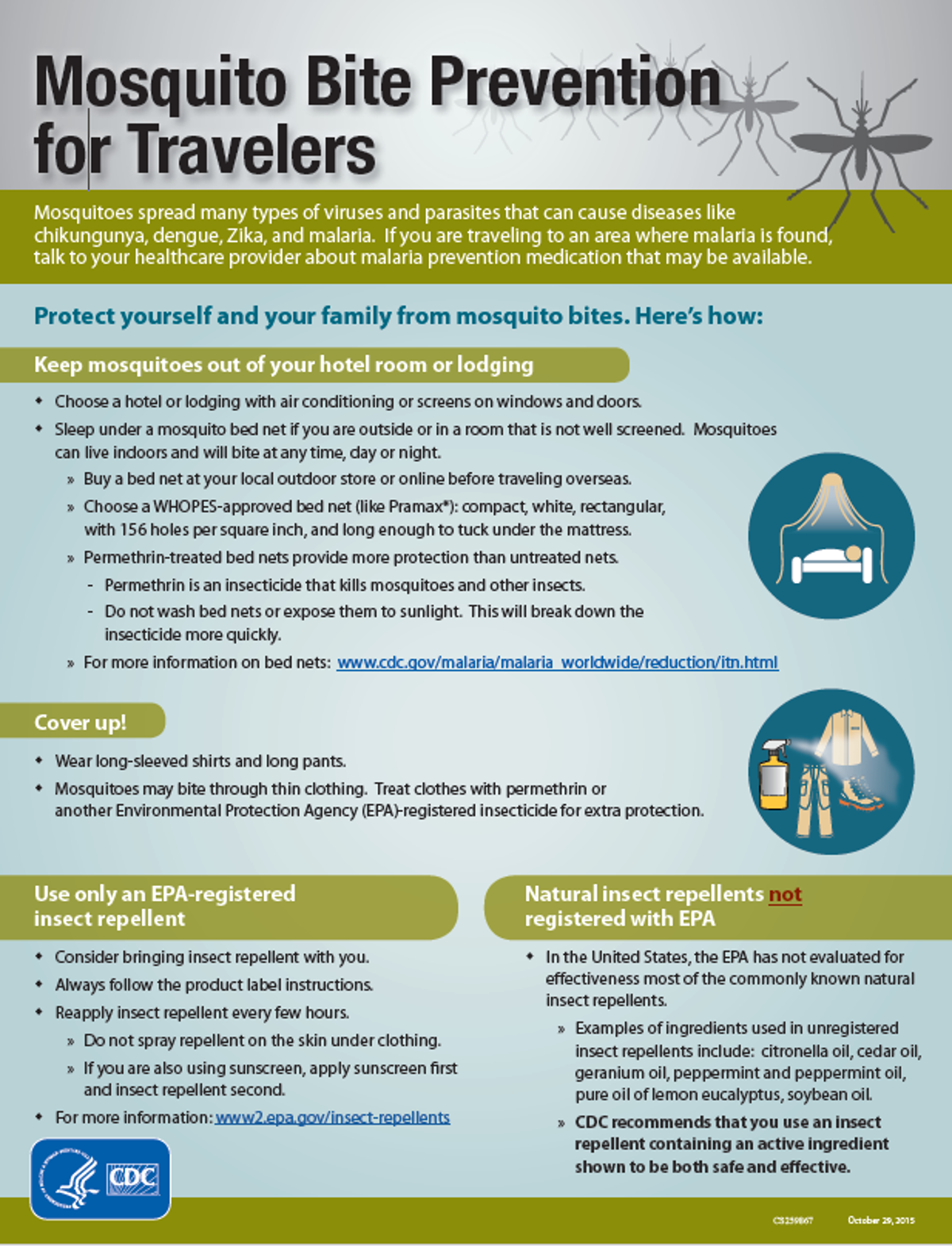
- Reduce the risk of importation of the Zika virus – travellers to countries with the Zika virus infection are advised to protect themselves from mosquito bites.
- Facilitate early detection of cases – returning travellers from affected areas are advised to seek medical attention if they develop symptoms of Zika such as fever, skin rashes, joint and muscle pains, headaches and red eyes.
- Contain the spread of Zika virus infection – confirmed cases will be admitted to a public hospital until they recover and test negative for the virus. Admitting them into a single room at the hospital will also minimise their risk of being bitten by mosquitoes while they are carrying the virus, which may result in further local transmission.
Further information
- Travellers to countries with local transmission of the Zika virus should take precautions and protect themselves from mosquito bites by:
- Wearing long sleeves, long trousers and/or appropriate covering clothing
- Applying insect-repellent . Sleeping under mosquito nets or in rooms with wire-mesh screens to keep out mosquitoes.
If travellers to such countries become unwell, they should seek medical attention promptly. Pregnant women should reconsider their travel plans to countries with ongoing outbreaks and local transmission.
Travellers who have returned from affected areas should monitor their health for the next 14 days and consult a doctor if they have any symptoms of Zika, such as fever, skin rashes, joint and muscle pains, headaches and red eyes. They should inform the doctor of the areas that they have travelled to.
In countries where mosquitos are an on-going problem, the following ‘5-step Mozzie Wipeout’ has proved worthwhile:
- Changing water in vases and bowls on alternate days
- Removing water from flower pot plates on alternate days
- Turning over all water storage containers
- Covering bamboo pole holders when not in use
- Keeping gutters clear from blockages and using appropriate insecticide in roof gutters monthly.

IMCA Safety Flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing lessons to be more easily learnt for the benefit of the entire offshore industry.
The effectiveness of the IMCA Safety Flash system depends on the industry sharing information and so avoiding repeat incidents. Incidents are classified according to IOGP's Life Saving Rules.
All information is anonymised or sanitised, as appropriate, and warnings for graphic content included where possible.
IMCA makes every effort to ensure both the accuracy and reliability of the information shared, but is not be liable for any guidance and/or recommendation and/or statement herein contained.
The information contained in this document does not fulfil or replace any individual's or Member's legal, regulatory or other duties or obligations in respect of their operations. Individuals and Members remain solely responsible for the safe, lawful and proper conduct of their operations.
Share your safety incidents with IMCA online. Sign-up to receive Safety Flashes straight to your email.